This blog post explores the state of data streaming for manufacturing. The evolution of industrial IoT, manufacturing 4.0, and digitalized B2B and customer relations require modern, open, and scalable information sharing. Data streaming allows integrating and correlating data in real-time at any scale. I look at trends like software-defined manufacturing and how data streaming helps modernize and innovate the entire engineering and sales lifecycle. The foci are trending enterprise architectures in the manufacturing industry and data streaming customer stories from BMW, Mercedes, Michelin, or Siemens. A complete slide deck and on-demand video recording are included.

General trends in the manufacturing industry
Researchers, analysts, startups, and last but not least, labs and the first real-world rollouts of traditional players show a few upcoming trends in the manufacturing industry:
- Software-defined manufacturing (see the “SDM4FZI” research project of the German Federal Ministry of Economics and Climate Protection, BMWK)
- Industry 4.0 and closed-loop manufacturing (see a great video recording from the research company “IoT Analytics”
- Automation and robotics (see a recent McKinsey report from January 2023)
Let’s explore the goals and impact of these trends.
Software-defined manufacturing
Software-defined manufacturing for the vehicle and supplier industry (SDM4FZI) is a German research project exploring the vision and future of significantly digitalized and automated manufacturing processes across the supply chain.
The four fundamental principles are on the wish list of every factory manager and shop floor team:
- Versatile: Highly versatile production systems with simultaneous control of complexity through virtualization
- Continuous: Continuity of the data chain from planning to operation (life cycle) and from the sensor to the cloud
- Automated: Fully automated software development process from requirements analysis and testing to distribution and execution in the digital factory
- Optimized: Risk-free optimization of applications in the virtual factory before deployment in the real world
The primary goal is a lot size of 1 and flexible, adaptive manufacturing leveraging digitalization with digital twins along the entire engineering and production process.
Industry 4.0 and closed-loop manufacturing
Closed-loop manufacturing means the synchronization of product lifecycle activities with product performance. The research company IoT Analytics describes the principle in a nice diagram:
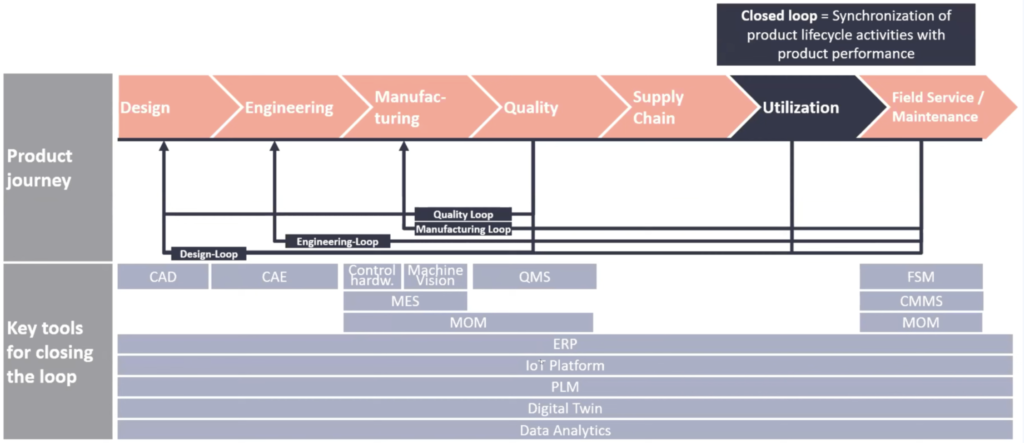
Information is connected and shared bi-directionally across the product journey from design and engineering across the entire production line up to aftersales. The following video explores the details:
Unlocking the industrial potential of robotics and automation
Industrial companies are set to spend heavily on robotics and automation. Industrial-company executives expect benefits in output quality, efficiency, and uptime. McKinsey published a great analysis of the investment and benefits of robotics and automation:
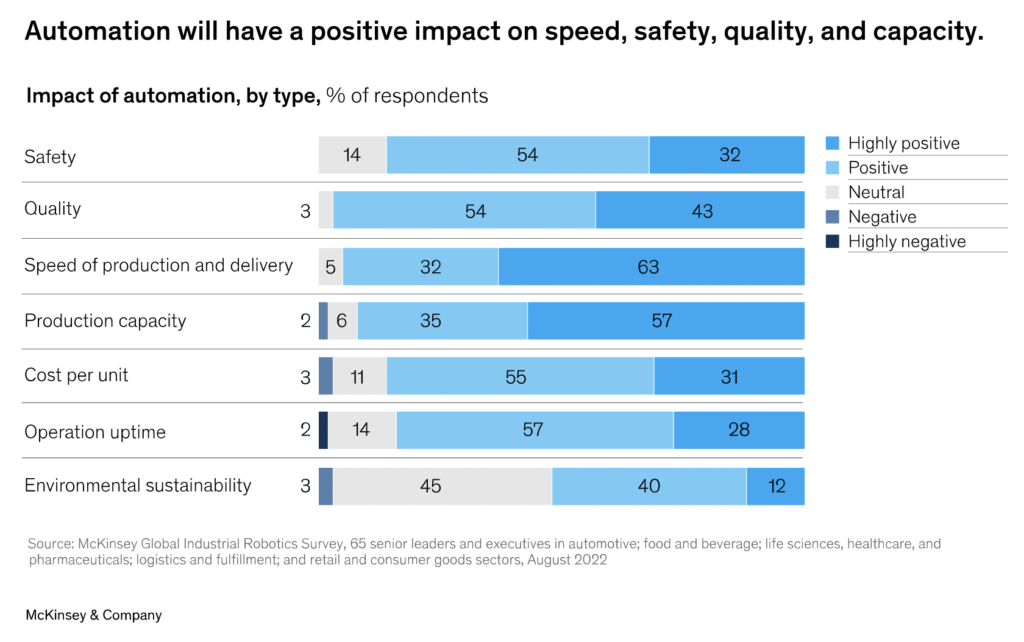
Robotics and automation implicitly include digitalizing the entire manufacturing process: the shop floor level production line and the integration with MES, ERP, and the rest of the IT world, like analytics, business intelligence, customer 360, etc.
Data streaming in manufacturing
Adopting trends like software-defined manufacturing and robotic automation is only possible if manufacturers can provide and correlate information at the right time in the proper context. Real-time, which means using the information in milliseconds, seconds, or minutes, is almost always better than processing data later (whatever later means):
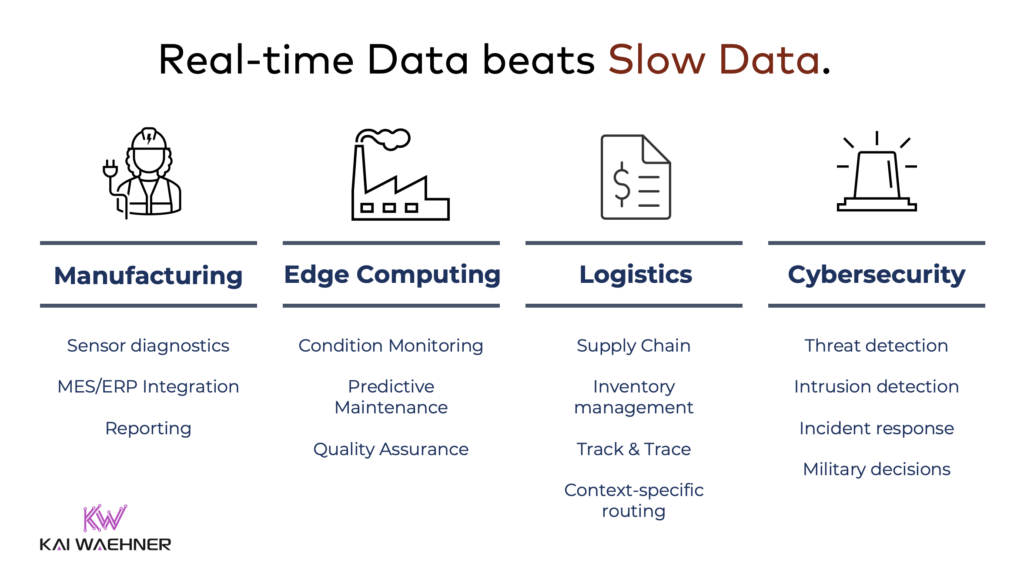
Data streaming combines the power of real-time messaging at any scale with storage for true decoupling, data integration, and data correlation capabilities. Apache Kafka is the de facto standard for data streaming.
“Apache Kafka in Manufacturing and Industry 4.0” is a good article for starting with an industry-specific point of view on data streaming.
Just-in-time manufacturing with data streaming
An adaptive manufacturing strategy starts with real-time data:
- Just-in-time (JIT) vs. make to forecast
- Fixed vs. variable price contracts
- Build vs. buy plant capacity
- Staffed vs. lights-out third shift
- Linking vs. not linking prices for materials and finished goods
Data streaming shines for such a use case as it can take real-time information of robots or sensors and correlate it with data of MES and ERP systems. For instance, almost every customer I talk to integrates Kafka with the SAP ecosystem.
This is just one example. Data streaming with the Apache Kafka ecosystem and cloud services are used throughout the manufacturing process, supply chain, and after-sales. Search my blog for various articles related to this topic: Search Kai’s blog.
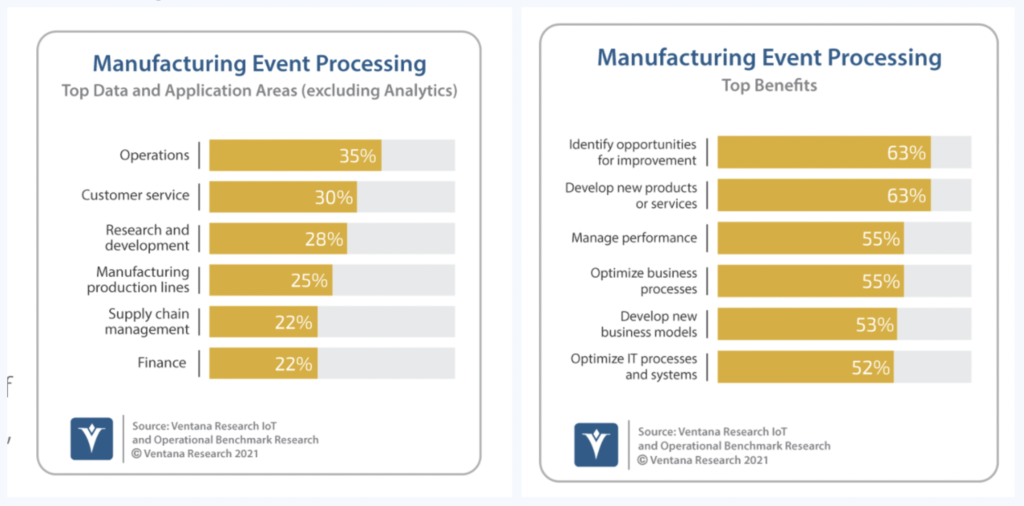
Top benefits of event stream processing for manufacturing
Ventana Research defined the top data and application areas (excluding analytics) for event stream processing. They explored the top benefits:
Architecture Trends
The manufacturing applies various trends for enterprise architectures for cost, flexibility, security, and latency reasons. The three major topics I see these days at customers are:
- IT deployments everywhere (edge, hybrid, multi-cloud)
- Real-time analytics at the shop floor level
- Data consistency across real-time and batch systems
Everywhere: Data streaming across edge and cloud
The following diagram shows an architecture from the shipping industry. IT workloads run where it makes most sense, like fully managed in the cloud, traditional software in the data center, IT workloads at the edge, or embedded into a machine or IoT device:
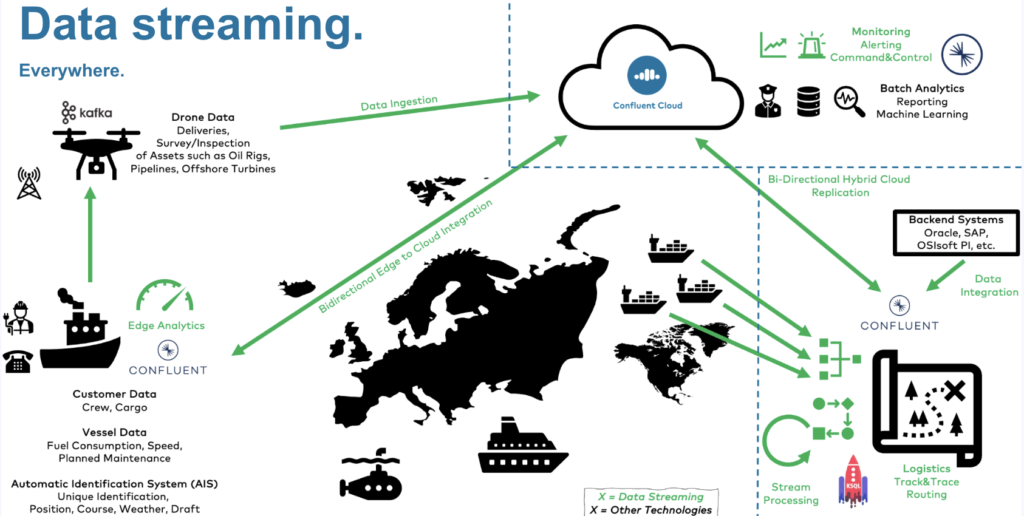
Data synchronization between the different things, sites, and regions is critical. Data streaming enables a reliable and scalable real-time replication between different technologies, APIs, and communication paradigms.
Analytics: Machine learning applied to the shop floor and IoT workloads
Data streaming enables many use cases from OT and shop floor level to customer-facing aftersales and service management. One of the most critical scenarios is low-latency analytics for condition monitoring and predictive maintenance.
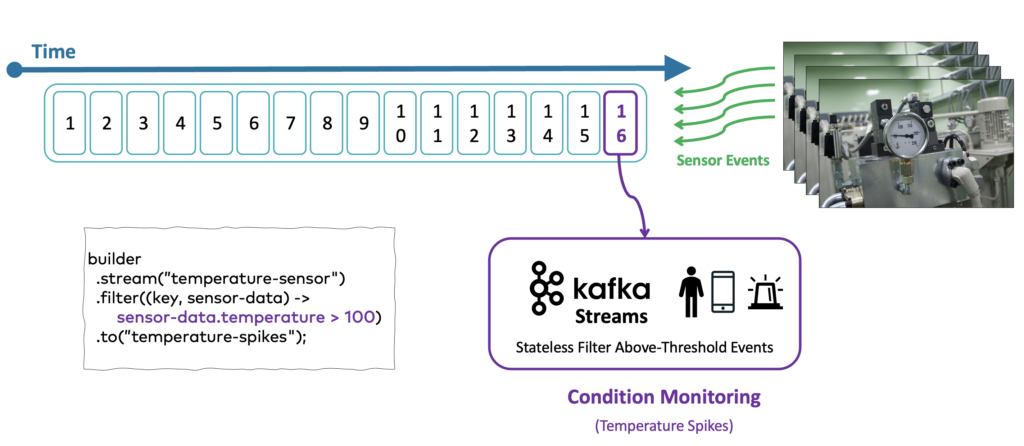
Straightforward stream processing in stateless applications is already powerful. The following diagram shows condition monitoring for temperature spikes in real time:
More advanced stateful streaming analytics allows continuous aggregation and correlation of events from one or more machines, for instance, to create a constant sliding window over the last 60 minutes to detect anomalies:
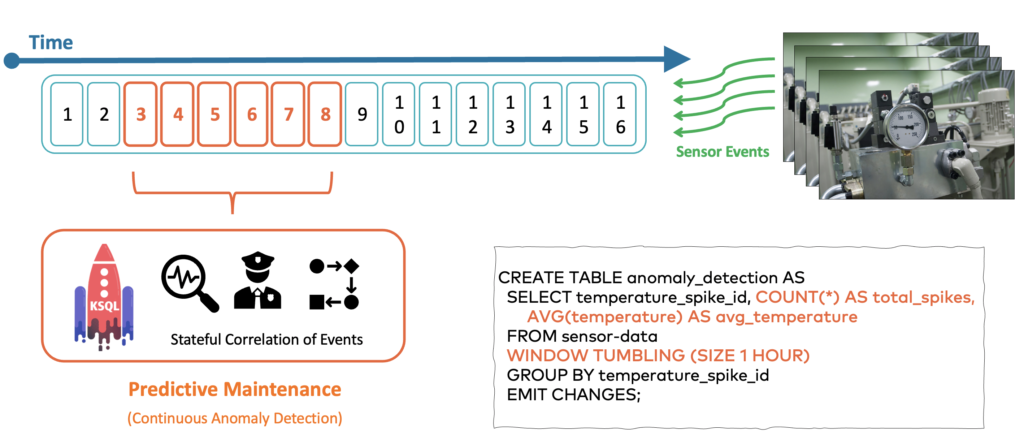
Such a scenario can implement business logic or even deploy analytic models that the data science team trained in the cloud with data streaming and machine learning in the data lake.
Data consistency: Integration and correlation between real-time and batch systems
More and more people understand that a real differentiator of data streaming is its capability to work with real time, batch, and request-response APIs at the same time to ensure data consistency across different technologies and communication paradigms:
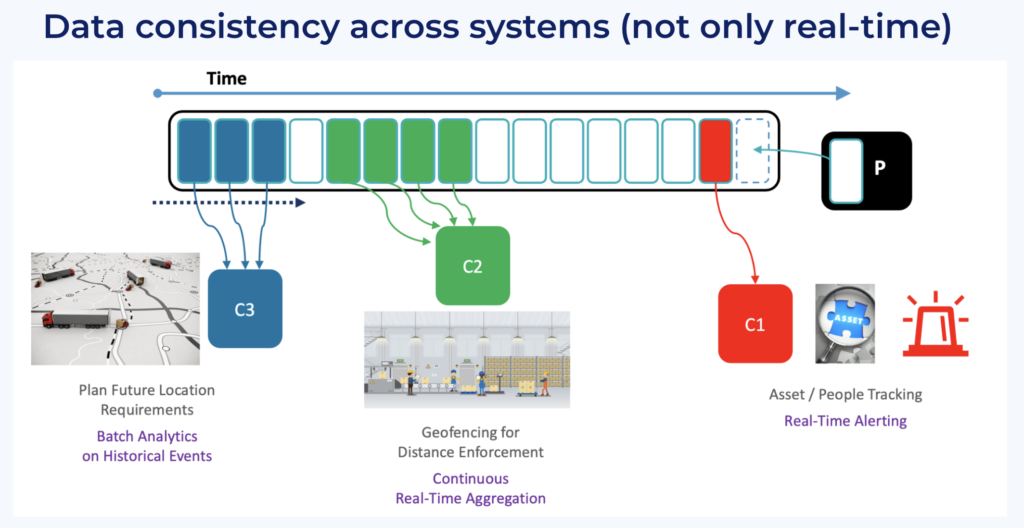
Not every system is or will be real time. The storage capability of the commit log appends data and stores it for as long as needed (hours, days, years). Besides real-time consumption, batch applications and web APIs can reprocess historical data in guaranteed order for reporting/analytics or interactive queries.
New customer stories for data streaming in manufacturing
So much innovation is happening in the manufacturing industry. Automation and digitalization change how car makers, energy providers, and other enterprises leverage data to increase overall equipment effectiveness (OEE) and improve the customer experience.
Most enterprises use a cloud-first (but still hybrid) approach to improve time-to-market, increase flexibility, and focus on business logic instead of operating IT infrastructure.
Here are a few customer stories from worldwide manufacturers across industries:
- BMW: From smart factories to the cloud
- Michelin: From shop floor to customer service
- 50Hertz: From monolithic SCADA to cloud-native IoT
- Siemens: From SAP ERP on-premise to Salesforce CRM in the cloud
- Mercedes: From manual business processes to seamless customer 360
Find more details about these case studies in the below slide deck.
Resources to learn more
This blog post is just the starting point. Learn more in the following on-demand webinar recording, the related slide deck, and further resources, including pretty cool lightboard videos about use cases.
On-demand video recording
The video recording explores the manufacturing industry’s trends and architectures for data streaming. The primary focus is the data streaming case studies from BMW, Michelin, 50Hertz, Siemens, and Mercedes:
Slides
If you prefer learning from slides, check out the deck used for the above recording:
Fullscreen ModeCase studies and lightboard videos for data streaming in the manufacturing industry
The state of data streaming for manufacturing in 2023 is fascinating. New use cases and case studies come up every month. This includes better data governance across the entire organization, collecting data from the IoT and OT worlds in real-time, customer service and aftersales, data sharing and B2B partnerships with suppliers and sales partners for new business models, and so many more scenarios.
We recorded lightboard videos showing the value of data streaming simply and effectively. These five-minute videos explore the business value of data streaming, related architectures, and customer stories:
And this is just the beginning. Every month, we will talk about the status of data streaming in a different industry. Manufacturing was the first. Next is financial services, then retail, and so on…
Let’s connect on LinkedIn and discuss it! Join the data streaming community and stay informed about new blog posts by subscribing to my newsletter.