Delivering a seamless and personalized customer experience across all touchpoints is essential for staying competitive in today’s rapidly evolving retail and e-commerce landscape. Unified commerce integrates all sales channels and backend systems into a single platform to ensure real-time consistency in customer interactions, inventory management, and order fulfillment. Leveraging the power of data streaming with Apache Kafka and Apache Flink, businesses can harness real-time data streaming to build a comprehensive Customer 360 view and to enable instant insights and tailored experiences. This approach not only enhances operational efficiency but also drives customer loyalty by offering a truly unified and responsive shopping experience. This blog post explores how Kafka and Flink can be pivotal in achieving real-time Customer 360 in the unified commerce ecosystem and how it differs from traditional omnichannel approaches.

What is Unified Commerce?
Unified commerce is an approach that integrates all customer-facing channels and backend systems into a single platform, providing a seamless, consistent experience across every touchpoint, whether online, in-store, or via mobile. Unlike traditional multichannel or omnichannel strategies, where different channels might operate independently or with partial integration, unified commerce brings everything together in real time. This includes inventory management, customer data, order fulfillment, and payment processing, all managed by a central system.
Difference between Unified Commerce and Omnichannel?
While both unified commerce and omnichannel aim to provide a seamless customer experience across different channels, they differ in their approach to integration:
- Omnichannel: In an omnichannel strategy, businesses integrate multiple channels (such as online, in-store, and mobile apps) to create a consistent customer experience. However, these channels often run on separate systems, requiring middleware or manual processes to synchronize data across platforms. This can lead to delays, inconsistencies, and a fragmented view of the customer.
- Unified Commerce: Unified commerce takes omnichannel a step further by consolidating all channels into a single platform that operates in real-time. This means inventory, customer information, and order data are updated instantly across all touchpoints to provide a more cohesive and responsive experience. It eliminates the silos between channels, ensuring that customers have a truly unified experience, no matter where or how they interact with the brand.
Gartner: In-Store for Retail = Ground Control for Space Operations
“The retail store plays the same role as ground control for space operations” said. Joanne Joliet, Senior Director Analyst at Gartner. The following Gartner slide already implies how crucial hybrid connectivity and real-time correlation are to process data in real-time:
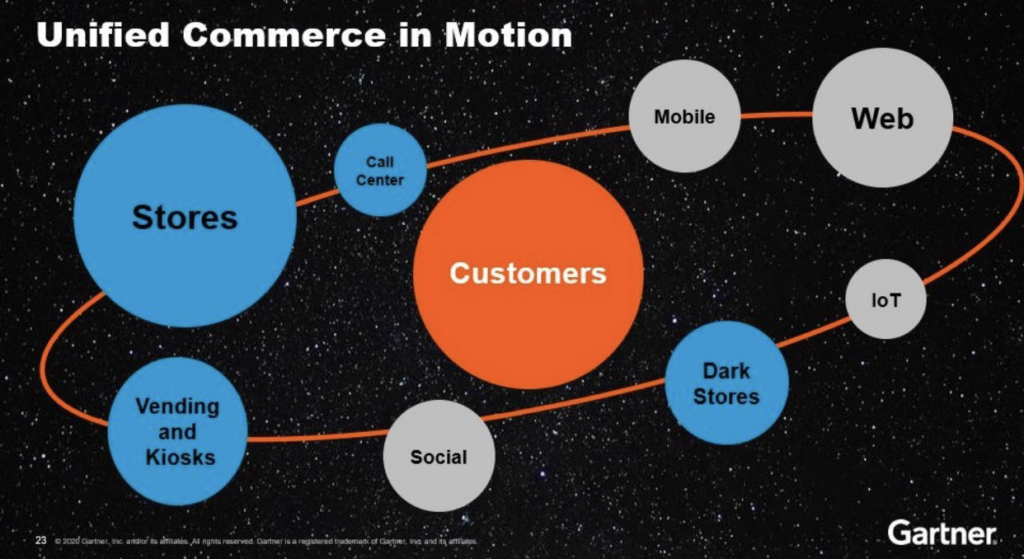
The summary of a Gartner IT Symposium/Xpo quotes a few interesting statements:
- “Even as online retail increased by 44% during the COVID-19 pandemic, physical retail stores are indispensable. 61% of shoppers prefer to return online orders to stores, which makes retail stores a key component of a retailer’s overall success.”
- “Stores need to be connected to reduce data latency and provide situational awareness. Smart checkout, robotic process automation, algorithmic retailing, contextualized real time pricing, conversational commerce are some of the technologies that can help achieve unified commerce.”
- “Retailers who create fluidity and flexibility by building a unified commerce ecosystem will be the ones who succeed.”
Relevant Industries
Unified commerce is relevant in industries where customer experience and channel integration are critical for success. These include:
- Retail: To provide a seamless shopping experience across online stores, physical locations, and mobile apps.
- Hospitality: Integrating booking, dining, and customer service channels to enhance the guest experience.
- Food and Beverage: Managing orders from various sources like in-store, online, and delivery apps, with consistent inventory and customer data.
- E-commerce: Ensuring that online sales platforms are fully integrated with inventory, logistics, and customer service.
- Healthcare: Unifying patient management systems, appointment scheduling, telemedicine, and billing.
How can Data Streaming with Apache Kafka and Flink help with Unified Commerce?
Data streaming with Apache Kafka and Apache Flink can significantly enhance unified commerce by enabling real-time data integration, processing, and analysis across various channels and backend systems.
- Real-Time Inventory Management: Kafka can stream real-time inventory updates from different channels (e.g., online stores, physical stores, warehouses) into a unified platform. Flink can then process this data to ensure that inventory levels are consistently accurate across all touchpoints, reducing stockouts and overselling.
- Personalized Customer Experience: Kafka can stream customer interaction data from various sources, like websites, mobile apps, and in-store transactions. Flink can process this data in real time to provide personalized recommendations, targeted promotions, and a consistent shopping experience across channels.
- Order Tracking and Fulfillment: Kafka can stream order status updates from various fulfillment centers. Flink can process these streams to provide customers with real-time updates on their order status, ensuring transparency and enhancing the customer experience.
- Fraud Detection: Kafka can stream transaction data in real time. Flink can analyze this data to detect patterns indicative of fraudulent activities. This allows businesses to respond instantly to potential threats, protecting both the business and its customers.
- Real-Time Analytics and Reporting: Kafka can collect data from all commerce activities. Flink can process and analyze this data in real time to generate up-to-date insights for decision-making. This enables businesses to adapt quickly to market trends, customer behaviors, and operational needs.
Here is an example of a hybrid retail architecture powered by an event-driven architecture using data streaming to enable Unified Commerce:
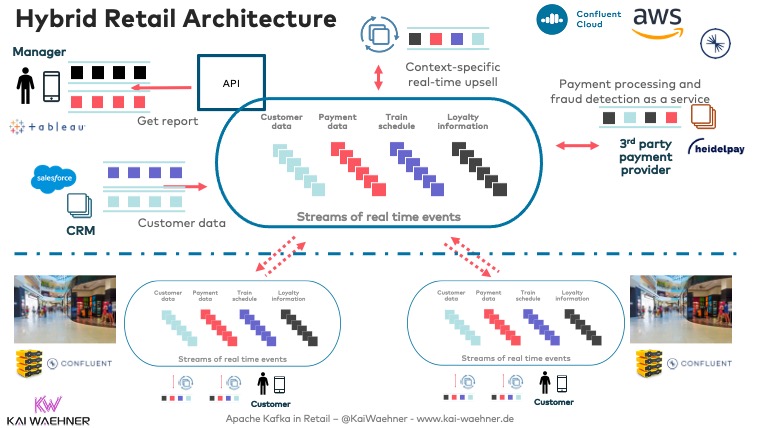
By leveraging Kafka and Flink, unified commerce platforms can achieve high responsiveness, scalability, and a seamless customer experience.
Build vs. Buy a Unified Commerce Platform?
When choosing between building a unified commerce platform or buying one, consider that building allows for tailored customization but requires significant time, resources, and expertise. Buying a pre-built solution offers quicker deployment and vendor support, though it may have limitations in flexibility, scalability, and cost efficiency.
BUY: Tools, Products and SaaS Cloud Services for Unified Commerce
Here are some tools, products, and SaaS solutions that support unified commerce:
- Salesforce Commerce Cloud: Provides a unified platform for managing e-commerce, in-store sales, and customer data.
- Shopify Plus: Offers a scalable platform that unifies online and offline sales, including robust POS integration.
- Oracle Retail: Integrates retail operations, including inventory management, e-commerce, and customer experience management.
- Lightspeed: A cloud-based platform for retail and hospitality businesses, offering POS, e-commerce, and inventory management.
- Square for Retail: Combines POS, online sales, and customer management in a unified platform, ideal for small to medium-sized businesses.
- Magento (Adobe Commerce): A customizable e-commerce platform that supports unified commerce by integrating online and offline sales channels.
- BigCommerce: A SaaS platform that helps businesses unify their sales across different channels, including online, in-store, and marketplaces.
- SAP Commerce Cloud: Part of the SAP C/4HANA suite, it integrates e-commerce, sales, marketing, and service into a unified platform.
- Cegid Retail Y2: A retail-focused solution that unifies POS, inventory, and e-commerce with real-time updates and customer insights.
The choice depends on your existing product portfolio and relationship with vendors. But keep in mind that emerging enterprise architecture trends such as event-driven architecture, microservices, data mesh, and data products enable a true decoupling for higher flexibility, cost-efficient product selection, and consistent data integration between different technologies, APIs, and cloud services. There is no need to implement everything in a monolithic architecture with tight vendor lock-in.
And even if you buy a “complete” Unified Platform with all the features you need, you still need to integrate with the rest of the software and IT applications, systems, and IoT interfaces in your enterprise architecture. Apache Kafka is the leading integration platform providing event-driven real-time communication, reliable transactional processing, and flexible deployment options to deploy in the public cloud or at the edge in a retail store.
BUILD: Stream Processing with Kafka and Flink Combined with Software Products
Nobody will build an entire unified commerce platform from scratch. This means way too high cost, much effort, and a slow rollout. Hence, the above-listed products are an excellent starting point to implement unified commerce.
Most organizations leverage data streaming with Kafka and Flink to connect independent products, SaaS services, and custom microservices.
By the way: Did you know that even several of the above-listed commercial Unified Commerce products and cloud services leverage data streaming under the hood of their platform? Like the end user, these platforms require flexibility, scalability, consistent integration, and real-time data processing. That’s where Apache Kafka became the de facto standard as the foundation of the enterprise architecture.
Vendors like Salesforce or Shopify heavily rely on Apache Kafka as the foundation of their internal enterprise architecture. Many public articles are available going into the details. Let’s go deeper into one example from the above list: BigCommerce.
BigCommerce: A Cloud-Native Unified Commerce Platform powered by Apache Kafka
BigCommerce is a Unified Commerce platform that enables merchants to create commerce solutions for B2B, B2C, Multi-Storefront, Omnichannel, Headless, and International.
The solution is built on top of a fully managed Confluent Cloud. BigCommerce migrated from open-source Kafka with zero downtime, no data loss, and the ability to auto-scale. The Unified Commerce platform processes 1.6 billion messages each day comprising e-commerce events such as visits, product page views, add to cart, checkouts, orders, etc.
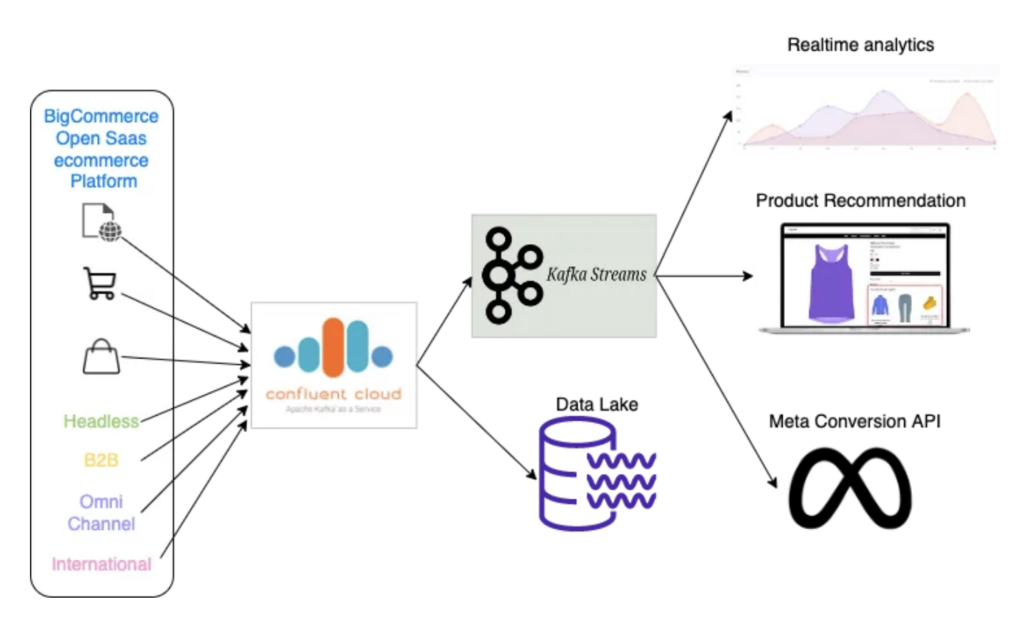
BigCommerce implements various retail use cases in different business units with Apache Kafka using fully managed Confluent Cloud, including:
- Real-time analytics and insights for merchants
- Server-side event transmission for Meta’s conversion APIs for social commerce and advertisements
- Bot filter exploration for fraud prevention using stream processing
- Continuous data ingestion into the data lake for batch analytics and model training
- AI and Machine Learning based real-time personalized product recommendations
Like BigCommerce, end users can either build their custom solution or leverage data streaming as the event-driven foundation to connect to a Unified Commerce platform and synchronize it with the other systems and databases in the enterprise architecture.
Apache Kafka and Flink to Enable Unified Commerce with Real-Time Customer 360
Unified commerce is a strategic approach that unifies all sales channels and backend systems into a single, integrated platform, enabling real-time data synchronization and a seamless customer experience across all touchpoints. It differs from omnichannel by eliminating the silos between channels, providing a more cohesive and responsive experience.
Unified commerce is relevant in industries like retail, hospitality, e-commerce, and healthcare, where customer experience is critical. A single platform cannot solve all problems. Flexibility, cost-efficiency, and the ability to innovate quickly with a fast time to market, leveraging innovative cloud services, requires the right enterprise architecture integration strategy.
An event-driven architecture powered by data streaming with Apache Kafka and Apache Flink can significantly enhance unified commerce by enabling real-time data processing and analysis across various channels and backend systems.
I published plenty of other retail articles that show data streaming use cases hybrid edge to cloud architectures, and success stories from enterprises around the world. Here are a few examples:
- The State of Data Streaming in the Retail Industry
- From Point of Sale (POS) at the Edge to Real-Time Inventory Management in the Cloud
- End-to-End Supply Chain with Data Consistency Leveraging Apache Kafka
- Data Streaming with Apache Kafka and Flink for Live and Social Commerce
What is your strategy to build a Unified Commerce platform? Which open-source frameworks, products, or cloud services do you use? What strategy does data streaming play? Let’s connect on LinkedIn and discuss it! Stay informed about new blog posts by subscribing to my newsletter.