In the world of data-driven applications, the rise of stream processing has changed how we handle and act on data. While traditional databases, data lakes, and warehouses are effective for many batch-based use cases, they fall short in scenarios demanding low latency, scalability, and real-time decision-making. This post explores the key concepts of stateless and stateful stream processing, using Kafka Streams and Apache Flink as examples. These principles apply to any stream processing engine, whether open-source or a cloud service. Let’s break down the differences, practical use cases, the relation to AI/ML, and the immense value stream processing offers compared to traditional data-at-rest methods.
Join the data streaming community and stay informed about new blog posts by subscribing to my newsletter and follow me on LinkedIn or X (former Twitter) to stay in touch.
Rethinking Data Processing: From Static to Dynamic
In traditional systems, data is typically stored first in a database or data lake and queried later for computation. This works well for batch processing tasks, like generating reports or dashboards. The process usually looks something like this:
- Store Data: Data arrives and is stored in a database or data lake.
- Query & Compute: Applications request data for analysis or processing at a later time with a web service, request-response API or SQL script.
However, this approach fails when you need:
- Immediate Action: Real-time responses to events, such as fraud detection.
- Scalability: Handling thousands or millions of events per second.
- Continuous Insights: Ongoing analysis of data in motion.
Enter stream processing—a paradigm where data is continuously processed as it flows through the system. Instead of waiting to store data first, stream processing engines like Kafka Streams and Apache Flink enable you to act on data instantly as it arrives.
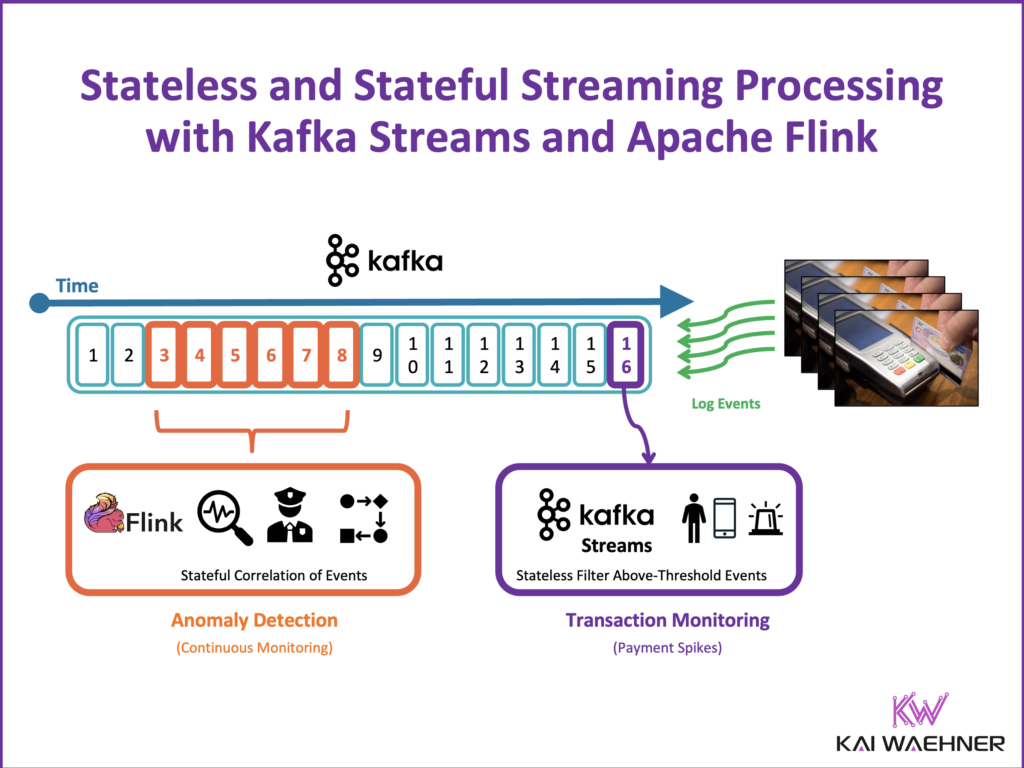
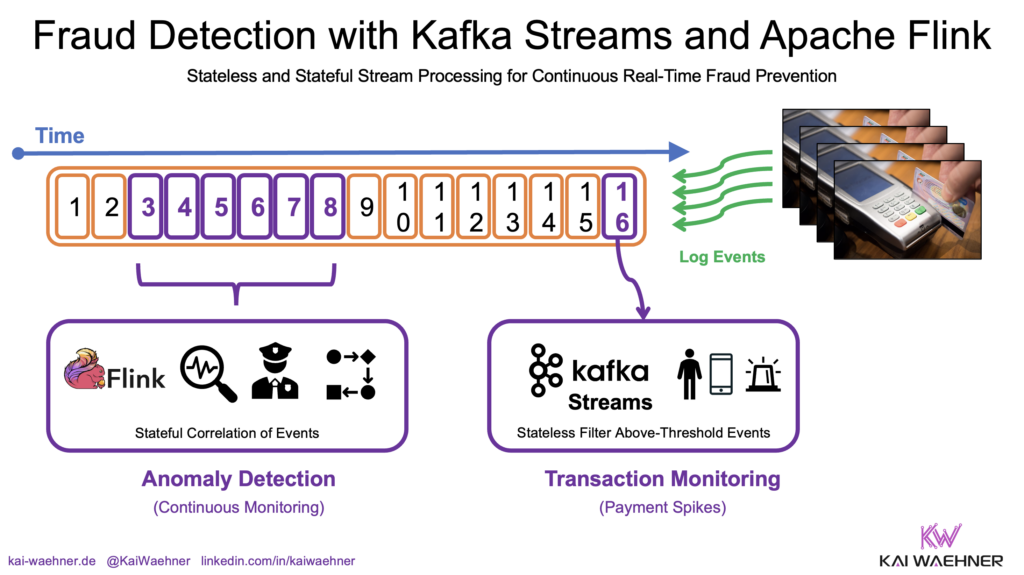
Use Case: Fraud Prevention in Real-Time
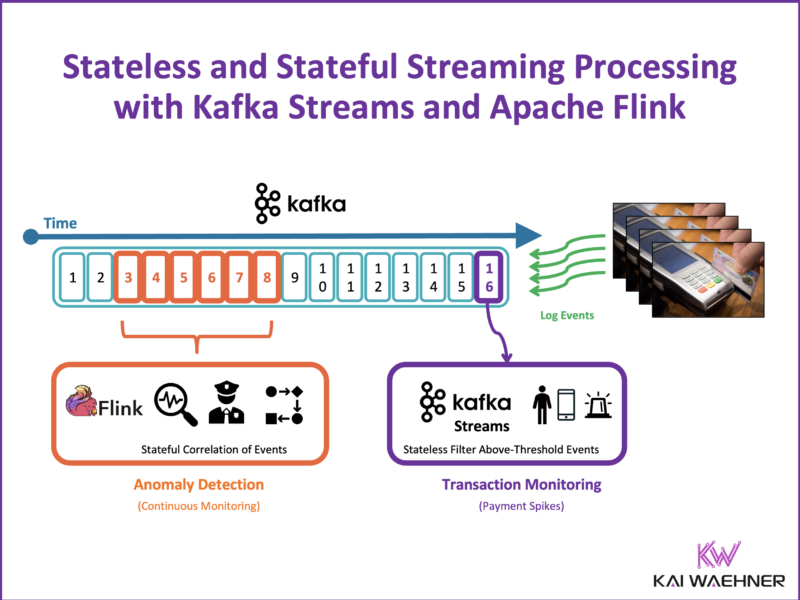
The blog post uses a fraud prevention scenario to illustrate the power of stream processing. In this example, transactions from various sources (e.g., credit card payments, mobile app purchases) are monitored in real time.

The system flags suspicious activities using three methods:
- Stateless Processing: Each transaction is evaluated independently, and high-value payments are flagged immediately.
- Stateful Processing: Transactions are analyzed over a time window (e.g., 1 hour) to detect patterns, such as an unusually high number of transactions.
- AI Integration: A pre-trained machine learning model is used for real-time fraud detection by predicting the likelihood of fraudulent activity.
This example highlights how stream processing enables instant, scalable, and intelligent fraud detection, something not achievable with traditional batch processing.
To avoid confusion: while I use Kafka Streams for stateless and Apache Flink for stateful in the example, both frameworks are capable of handling both types of processing.
Other Industry Examples of Stream Processing
- Predictive Maintenance (Industrial IoT): Continuously monitor sensor data to predict equipment failures and schedule proactive maintenance.
- Real-Time Advertisement (Retail): Deliver personalized ads based on real-time user interactions and behavior patterns.
- Real-Time Portfolio Monitoring (Finance): Continuously analyze market data and portfolio performance to trigger instant alerts or automated trades during market fluctuations.
- Supply Chain Optimization (Logistics): Track shipments in real time to optimize routing, reduce delays, and improve efficiency.
- Condition Monitoring (Healthcare): Analyze patient vitals continuously to detect anomalies and trigger immediate alerts.
- Network Monitoring (Telecom): Detect outages or performance issues in real time to improve service reliability.
These examples highlight how stream processing drives real-time insights and actions across diverse industries.
What is Stateless Stream Processing?
Stateless stream processing focuses on processing each event independently. In this approach, the system does not need to maintain any context or memory of previous events. Each incoming event is handled in isolation, meaning the logic applied depends solely on the data within that specific event.
This makes stateless processing highly efficient and easy to scale, as it doesn’t require state management or coordination between events. It is ideal for use cases such as filtering, transformations, and simple ETL operations where individual events can be processed with no need of historical data or context.
1. Example: Real-Time Payment Monitoring
Imagine a fraud prevention system that monitors transactions in real time to detect and prevent suspicious activities. Each transaction, whether from a credit card, mobile app, or payment gateway, is evaluated as it occurs. The system checks for anomalies such as unusually high amounts, transactions from unfamiliar locations, or rapid sequences of purchases.
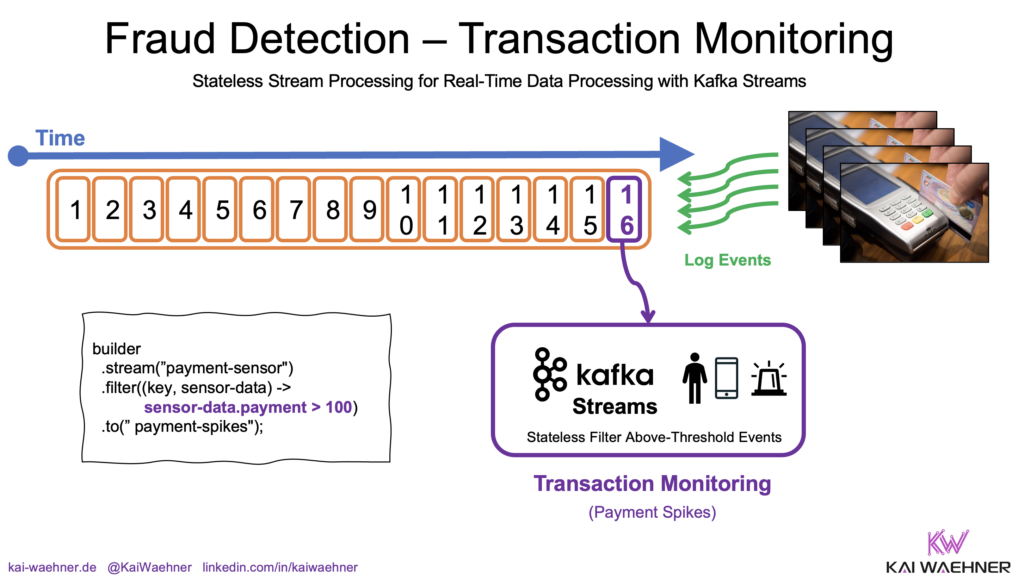
By analyzing these attributes instantly, the system can flag high-risk transactions for further inspection or automatically block them. This real-time evaluation ensures potential fraud is caught immediately, reducing the likelihood of financial loss and enhancing overall security.
You want to flag high-value payments for further inspection. In the following Kafka Streams example:
- Each transaction is evaluated as it arrives.
- If the transaction amount exceeds 100 (in your chosen currency), it’s sent to a separate topic for further review.
Java Example (Kafka Streams):
KStream<String, Payment> payments = builder.stream(“payments”);
payments.filter((key, payment) -> payment.getAmount() > 100)
.to(“high-risk-payments”);
Benefits of Stateless Processing
- Low Latency: Immediate processing of individual events.
- Simplicity: No need to track or manage past events.
- Scalability: Handles large volumes of data efficiently.
This approach is ideal for use cases like filtering, data enrichment, and simple ETL tasks.
What is Stateful Stream Processing?
Stateful stream processing takes it a step further by considering multiple events together. The system maintains state across events, allowing for complex operations like aggregations, joins, and windowed analyses. This means the system can correlate data over a defined period, track patterns, and detect anomalies that emerge across multiple transactions or data points.
2. Example: Fraud Prevention through Continuous Pattern Detection
In fraud prevention, individual transactions may appear normal, but patterns over time can reveal suspicious behavior.
For example, a fraud prevention system might identify suspicious behavior by analyzing all transactions from a specific credit card within a one-hour window, rather than evaluating each transaction in isolation.
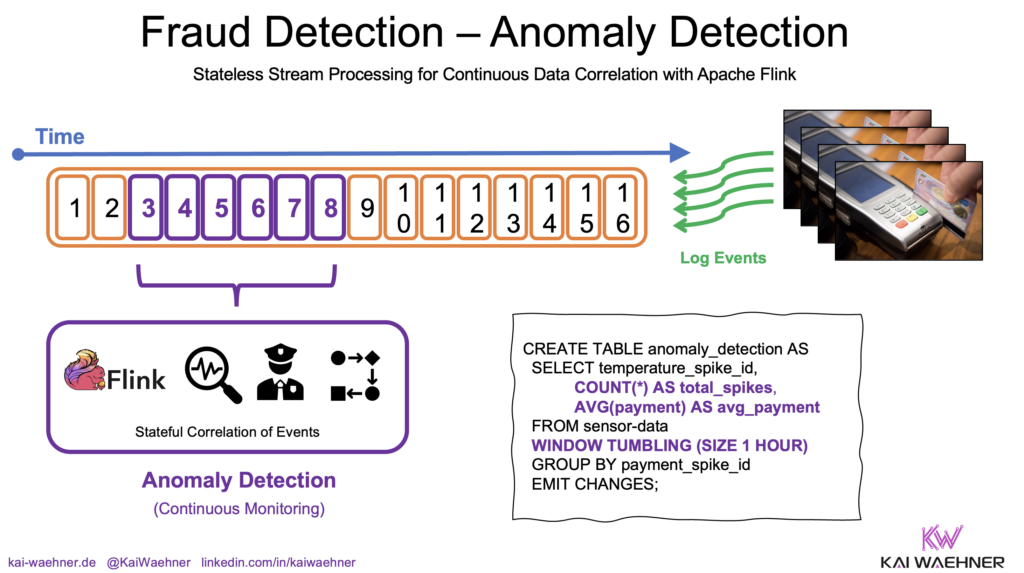
Let’s detect anomalies by analyzing transactions with Apache Flink using Flink SQL. In this example:
- The system monitors transactions for each credit card within a 1-hour window.
- If a card is used over 10 times in an hour, it flags potential fraud.
SQL Example (Apache Flink):
SELECT card_number, COUNT(*) AS transaction_count
FROM payments
GROUP BY TUMBLE(transaction_time, INTERVAL ‘1’ HOUR), card_number
HAVING transaction_count > 10;
Key Concepts in Stateful Processing
Stateful processing relies on maintaining context across multiple events, enabling the system to perform more sophisticated analyses. Here are the key concepts that make stateful stream processing possible:
- Windows: Define a time range to group events (e.g., sliding windows, tumbling windows).
- State Management: The system remembers past events within the defined window.
- Joins: Combine data from multiple sources for enriched analysis.
Benefits of Stateful Processing
Stateful processing is essential for advanced use cases like anomaly detection, real-time monitoring, and predictive analytics:
- Complex Analysis: Detect patterns over time.
- Event Correlation: Combine events from different sources.
- Real-Time Decision-Making: Continuous monitoring without reprocessing data.
Bringing AI and Machine Learning into Stream Processing
Stream processing engines like Kafka Streams and Apache Flink also enable real-time AI and machine learning model inference. This allows you to integrate pre-trained models directly into your data processing pipelines.
3. Example: Real-Time Fraud Detection with AI/ML Models
Consider a payment fraud detection system that uses a TensorFlow model for real-time inference. In this system, transactions from various sources — such as credit cards, mobile apps, and payment gateways — are streamed continuously. Each incoming transaction is preprocessed and sent to the TensorFlow model, which evaluates it based on patterns learned during training.
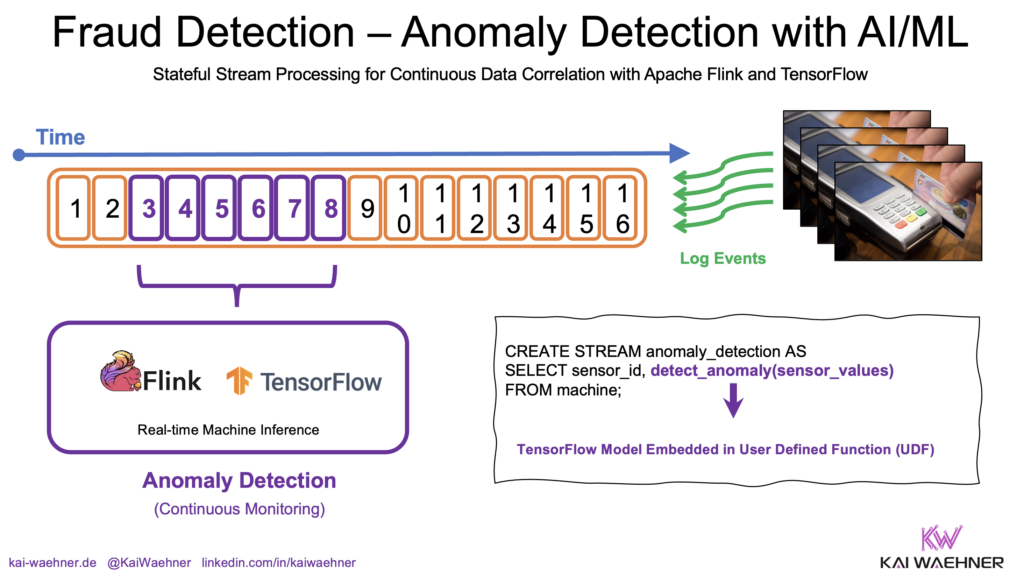
The model analyzes features like transaction amount, location, device ID, and frequency to predict the likelihood of fraud. If the model identifies a high probability of fraud, the system can trigger immediate actions, such as flagging the transaction, blocking it, or alerting security teams. This real-time inference ensures that potential fraud is detected and addressed instantly, reducing risk and enhancing security.
Here is a code example using Apache Flink’s Python API for predictive AI:
Python Example (Apache Flink):
def predict_fraud(payment):
prediction = model.predict(payment.features)
return prediction > 0.5stream = payments.map(predict_fraud)
Why Combine AI with Stream Processing?
Integrating AI with stream processing unlocks powerful capabilities for real-time decision-making, enabling businesses to respond instantly to data as it flows through their systems. Here are some key benefits of combining AI with stream processing:
- Real-Time Predictions: Immediate fraud detection and prevention.
- Automated Decisions: Integrate AI into critical business processes.
- Scalability: Handle millions of predictions per second.
Apache Kafka and Flink deliver low-latency, scalable, and robust predictions. My article “Real-Time Model Inference with Apache Kafka and Flink for Predictive AI and GenAI” compares remote inference (via APIs) and embedded inference (within the stream processing application).
For large AI models (e.g., generative AI or large language models), inference is often done via remote calls to avoid embedding large models within the stream processor.
Stateless vs. Stateful Stream Processing: When to Use Each
Choosing between stateless and stateful stream processing depends on the complexity of your use case and whether you need to maintain context across multiple events. The following table outlines the key differences to help you determine the best approach for your specific needs.
| Feature | Stateless | Stateful |
|---|---|---|
| Use Case | Simple Filtering, ETL | Aggregations, Joins |
| Latency | Very Low Latency | Slightly Higher Latency due o State Management |
| Complexity | Simple Logic | Complex Logic Involving Multiple Events |
| State Management | Not Required | Required for Context-aware Processing |
| Scalability | High | Depends on the Framework |
Read my article “Apache Kafka (including Kafka Streams) + Apache Flink = Match Made in Heaven” to learn more about choosing the right stream processing engine for your use case.
And to clarify again: while this article uses Kafka Streams for stateless and Flink for stateful stream processing, both frameworks are capable of handling both types.
Video Recording
Below, I summarize this content as a ten-minute video on my YouTube channel:
You are currently viewing a placeholder content from Default. To access the actual content, click the button below. Please note that doing so will share data with third-party providers.
Why Stream Processing is a Fundamental Change
Whether stateless or stateful, stream processing with Kafka Streams, Apache Flink, and similar technologies unlocks real-time capabilities that traditional databases simply cannot offer. From simple ETL tasks to complex fraud detection and AI integration, stream processing empowers organizations to build scalable, low-latency applications.
Investing in stream processing means:
- Faster Innovation: Real-time insights drive competitive advantage.
- Operational Efficiency: Automate decisions and reduce latency.
- Scalability: Handle millions of events seamlessly.
Stream processing isn’t just an evolution of data handling—it’s a revolution. If you’re not leveraging it yet, now is the time to explore this powerful paradigm. If you want to learn more, check out my light board video exploring the core value of Apache Flink:
You are currently viewing a placeholder content from Default. To access the actual content, click the button below. Please note that doing so will share data with third-party providers.
Stay ahead of the curve! Subscribe to my newsletter for insights into data streaming and connect with me on LinkedIn to continue the conversation.