Industrial enterprises are under pressure to modernize. They need to move faster, automate more, and adapt to constant change—without sacrificing reliability or control. Siemens Digital Industries is meeting this challenge head-on by combining software, edge computing, and cloud-native technologies into a new architecture. This blog explores how Siemens is using data streaming, modular design, and Shift Left thinking to enable real-time decision-making, improve data quality, and unlock scalable, reusable data products across manufacturing and logistics operations. A real-world example for industrial IoT, intralogistics and shop floor manufacturing illustrates the architecture and highlights the business value behind this transformation.

Join the data streaming community and stay informed about new blog posts by subscribing to my newsletter and follow me on LinkedIn or X (former Twitter) to stay in touch. And download my free book about data streaming use cases, including customer stories across all industries.
The Data Streaming Use Case Show: Episode #1 – Manufacturing and Automotive
These Siemens success stories are part of The Data Streaming Use Case Show, a new industry webinar series hosted by me.
In the first episode, we focus on the manufacturing and automotive industries. It features:
- Experts from Siemens Digital Industries and Siemens Healthineers
- The Founder of ‘IoT Use Case‘, a content and community platform focused on real-world industrial IoT applications
- Deep insights into how industrial companies combine OT, IT, cloud, and data streaming with the shift left architecture.
The series explores real-world solutions across industries, showing how leaders turn data into action through open architectures and real-time platforms.
Siemens Digital Industries: Company and Vision
Siemens Digital Industries is the technology and software arm of Siemens AG, focused on advancing industrial automation and digitalization. It empowers manufacturers and machine builders to become more agile, efficient, and resilient through intelligent software and integrated systems.
Its business model bridges the physical and digital worlds—combining operational technology (OT) with modern information technology (IT). From programmable logic controllers to industrial IoT, Siemens delivers end-to-end solutions across industries.
Today, the company is transforming itself into a software- and cloud-driven organization, focusing strongly on edge computing, real-time analytics, and data streaming as key enablers of modern manufacturing.
With edge and cloud working in harmony, Siemens helps industrial enterprises break up monoliths and develop toward modular, flexible architectures. These software-driven approaches make plants and factories more adaptive, intelligent, and autonomous.
Data Streaming at Industrial Companies
In industrial settings, data is continuously generated by machines, production systems, robots, and logistics processes. But traditional batch-oriented IT systems are not designed to handle this in real time.
To make smarter, faster decisions, companies need to process data as it is generated. That’s where data streaming comes in.
Apache Kafka and Apache Flink enable event-driven architectures. These allow industrial data to flow in real time, from edge to cloud, across hybrid environments.
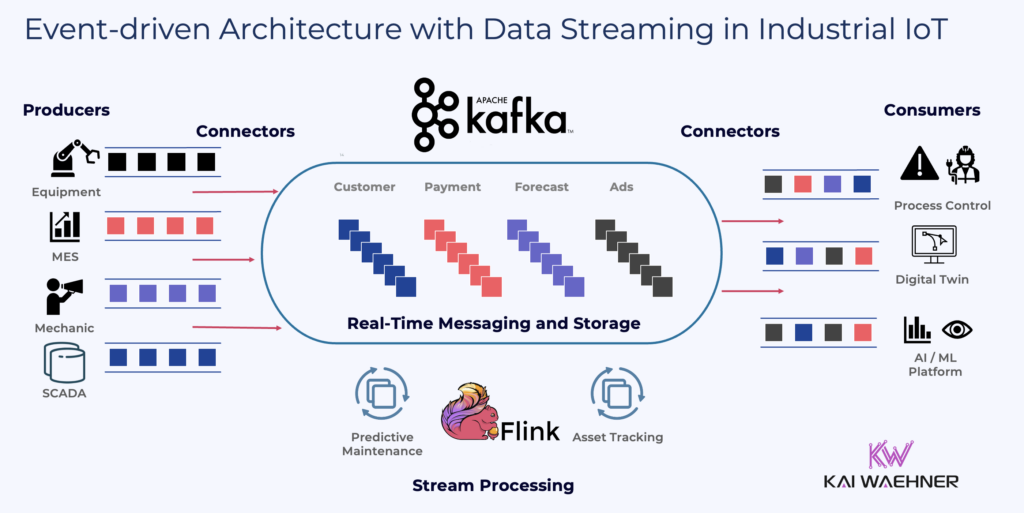
Check out my other blogs about use cases and architecture for manufacturing and Industrial IoT powered by data streaming.
Edge and Hybrid Cloud as a Standard
Modern industrial use cases are increasingly hybrid by design. Machines and controllers produce data at the edge. Decisions must be made close to the source. However, cloud platforms offer powerful compute and AI capabilities.
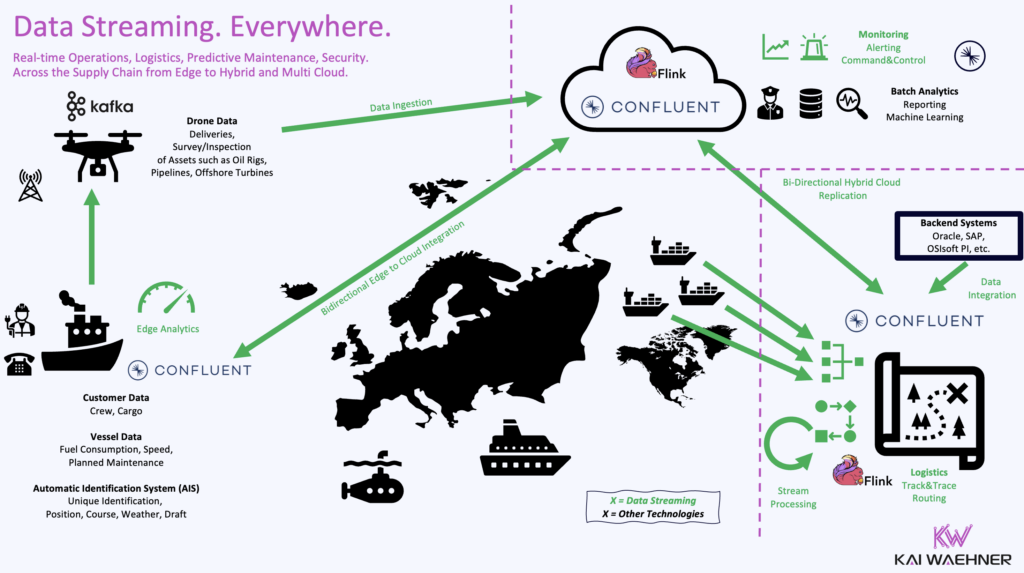
Siemens leverages edge devices to capture and preprocess data on-site. Data streaming with Confluent provides Siemens a real-time backbone for integrating this data with cloud-based systems, including Snowflake, SAP, Salesforce, and others.
This hybrid architecture supports low latency, high availability, and full control over data processing and analytics workflows.
The Shift Left Architecture for Industrial IoT
In many industrial architectures, Kafka has traditionally been used to ingest data into analytics platforms like Snowflake or Databricks. Processing, transformation, and enrichment happened late in the data pipeline.
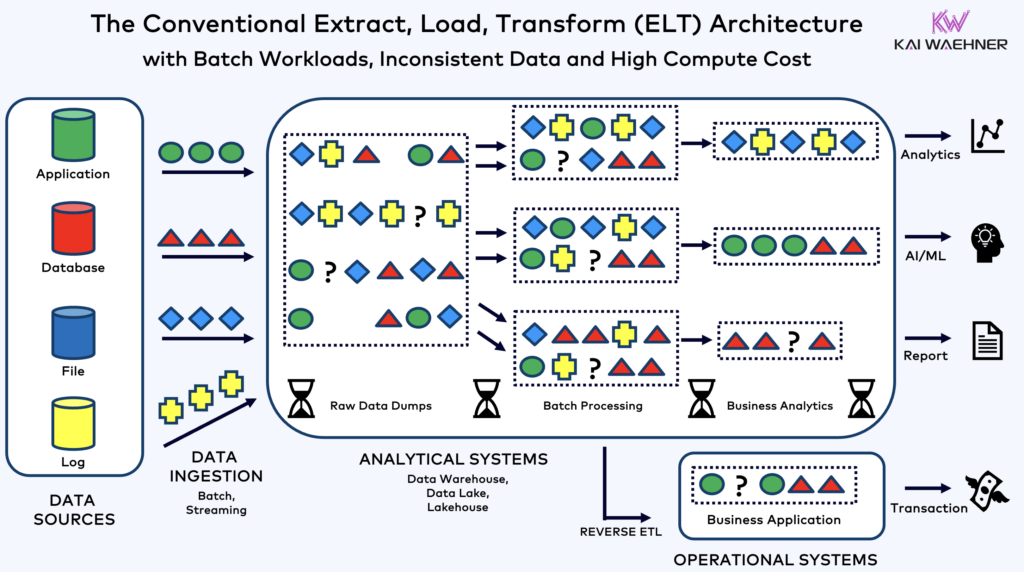
But Siemens is shifting that model.
The Shift Left Architecture moves processing closer to the source, directly into the streaming layer. Instead of waiting to transform data in a data warehouse, Siemens now applies stream processing in real time, using Confluent Cloud and Kafka topics.
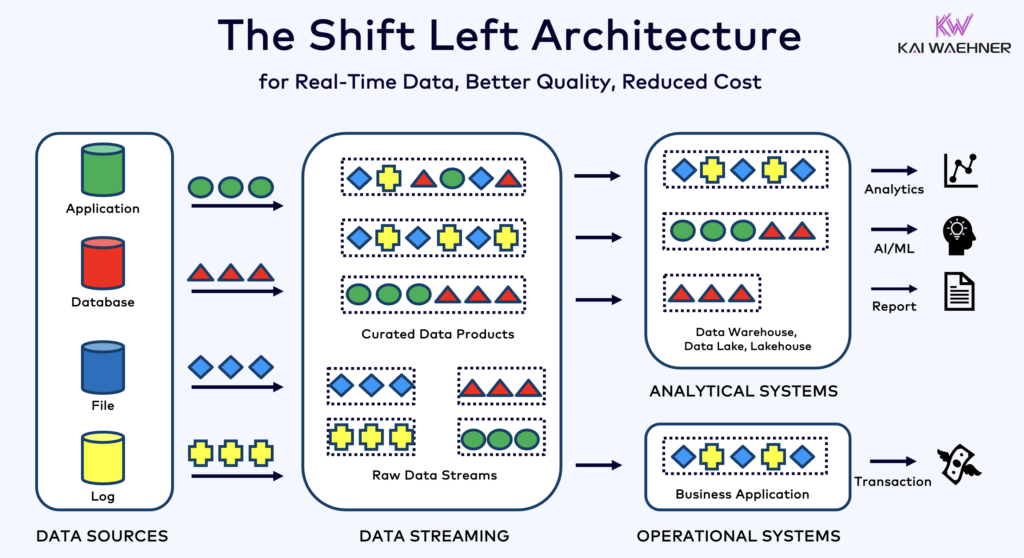
This shift enables faster decision-making, better data quality, and broader reuse of high-quality data across both analytical and operational systems.
For a deeper look at how Shift Left is transforming industrial architectures, read the full article about the Shift Left Architecture with Data Streaming.
Siemens Data Streaming Success Story: Modular Intralogistics Platform
A key example of this new architecture is Siemens’ Modular Intralogistics Platform, used in manufacturing plants for material handling and supply chain optimization. I explored the shift left architecture in our data streaming use case show with Stefan Baer, Senior Key Expert – Data Streaming at Siemens IT.
Traditionally, intralogistic systems were tightly coupled, with rigid integrations between
- Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP): Order management, master data
- Manufacturing Operations Management (MOM): Production scheduling, quality, maintenance
- Warehouse Execution System (EWM): Inventory, picking, warehouse automation
- Execution Management System (eMS): Transport control, automated guided vehicle (AGV) orchestration, conveyor logic
The new approach breaks this down into package business capabilities—each one modular, orchestrated, and connected through Confluent Cloud.
Key benefits:
- Real-time orchestration of logistics operations
- Automated material delivery—no manual reordering required
- ERP and MOM systems integrated flexibly via Kafka
- High adaptability through modular components
- GenAI used for package station load optimization
Stream processing with Apache Flink transforms events in motion. For example, when a production order changes or material shortages occur, the system reacts instantly—adjusting delivery routes, triggering alerts, or rebalancing station loads using AI.
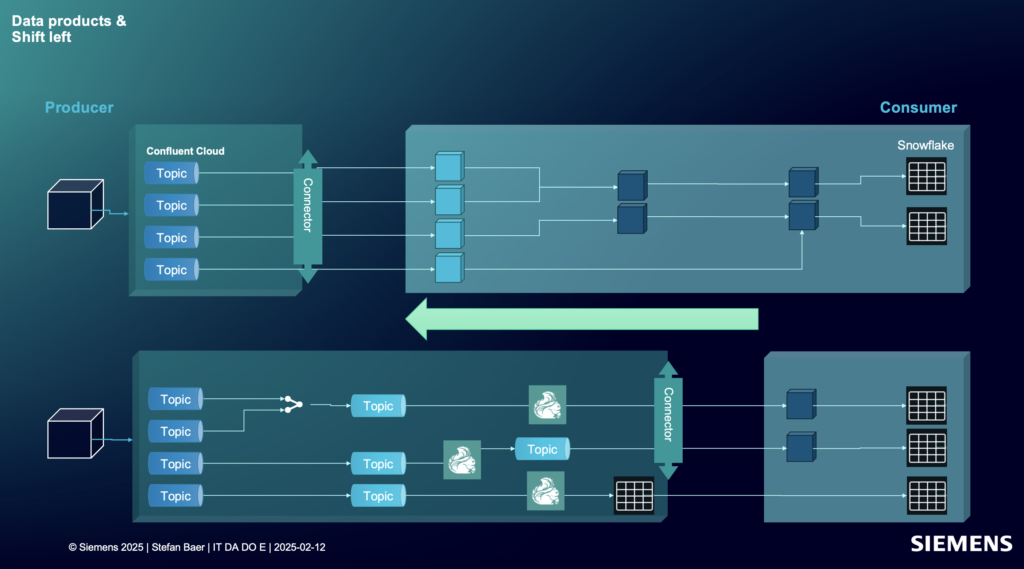
Architecture: Data Products + Shift Left
At the heart of the solution is a combination of data products and stream processing:
- Kafka Topics serve as real-time interfaces and persistency layer between business domains.
- Confluent Cloud hosts the event streaming infrastructure as a fully-managed service with low latency, elasticity, and critical SLAs.
- Stream processing with serverless Flink logic enriches and transforms data in motion.
- Snowflake receives curated, ready-to-use data for analytics.
- Other operational and analytical downstream consumers—such as GenAI modules or shop floor dashboards—access the same consistent data in real time.
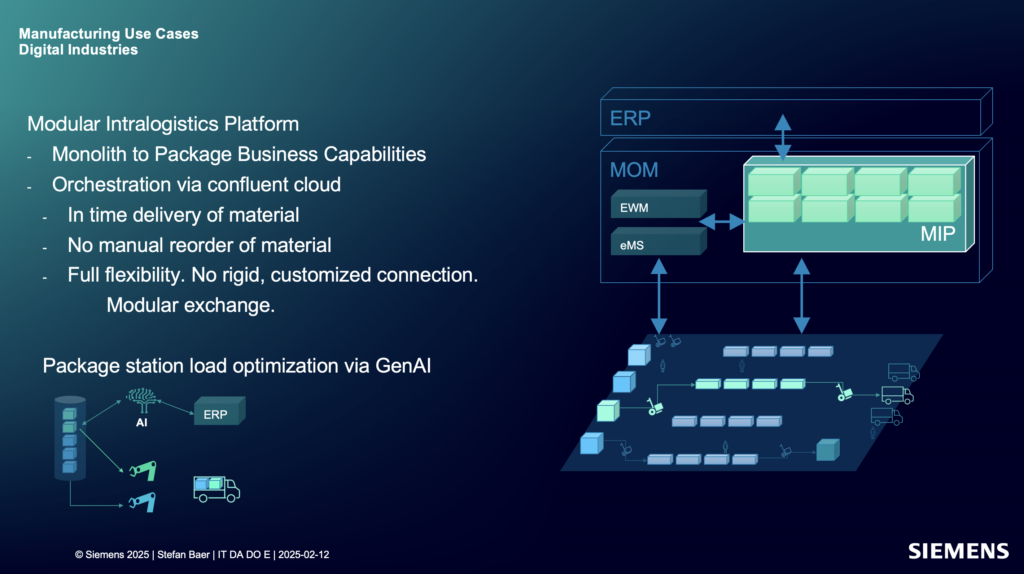
This reuse of data products ensures consistent semantics, reduces duplication, and simplifies governance.
By processing data earlier in the pipeline, Siemens improves both data quality and system responsiveness. This model replaces brittle, point-to-point integrations with a more sustainable, scalable platform architecture.
Business Value of Data Streaming and Shift Left at Siemens Digital Industries
The combination of real-time data streaming, modular data products, and Shift Left design principles unlocks significant value:
- Faster response to dynamic events in production and logistics
- Improved operational resilience and agility
- Higher quality data for both analytics and AI
- Reuse across multiple consumers (analytics, operations, automation)
- Lower integration costs and easier scaling
This approach is not just technically superior—it supports measurable business outcomes like shorter lead times, lower stock levels, and increased manufacturing throughput.
Siemens Healthineers: Shift Left with IoT, Data Streaming, AI/ML, Confluent and Snowflake in Manufacturing and Healthcare
In a recent blog post, I explored how Siemens Healthineers uses Apache Kafka and Flink to transform both manufacturing and healthcare with a wide range of data streaming use cases. From predictive maintenance to real-time logistics, their approach is a textbook example of how to modernize complex environments with an event-driven architecture and data streaming—even if they don’t explicitly label it “shift left.”
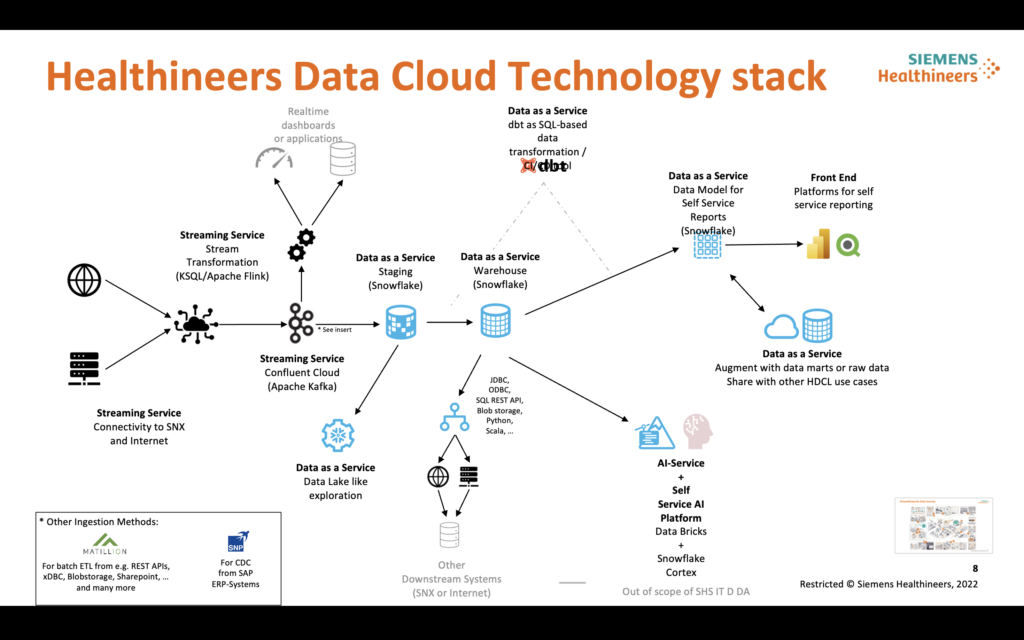
Their architecture enables proactive decision-making by pushing real-time insights and automation earlier in the process. Examples include telemetry streaming from medical devices, machine integration with SAP and KUKA robots, and logistics event streaming from SAP for faster packaging and delivery. Each use case shows how real-time data—combined with cloud-native platforms like Confluent and Snowflake—improves efficiency, reliability, and responsiveness.
Just like the intralogistics example from Siemens Digital Industries, Healthineers applies shift-left thinking by enabling teams to act on data sooner, reduce latency, and prevent costly delays. This approach enhances not only operational workflows but also outcomes that matter, like patient care and regulatory compliance.
This is shift left in action: embedding intelligence and quality controls early, where they have the greatest impact.
Rethinking Industrial Data Architectures with Data Streaming and Shift Left Architecture
Siemens Digital Industries is demonstrating what’s possible when you rethink the data architecture beyond just analytics in a data lake.
With data streaming leveraging Confluent Cloud, data products for modular software, and a Shift Left approach, Siemens is transforming traditional factories into intelligent, event-driven operations. A data streaming platform based on Apache Kafka is no longer just an ingestion layer. It is a central nervous system for real-time processing and decision-making.
This is not about chasing trends. It’s about building resilient, scalable, and future-proof industrial systems. And it’s just the beginning.
To learn more, watch the on-demand industry use case show with Siemens Digital Industries and Siemens Healthineers or connect with us to explore what data streaming can do for your organization.
Let’s connect on LinkedIn and discuss it! Stay informed about new blog posts by subscribing to my newsletter. And download my free book about data streaming use cases.